Welcome to another in-depth exploration at TheKitchenApplianceDad.com, where today we delve into the world of refrigerants, specifically focusing on Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) and their flammability characteristics. In recent years, the shift towards using HFOs in refrigerators and air conditioners has been significant due to their environmental benefits and safety features, particularly their reduced flammability compared to traditional refrigerants.
Refrigerants are substances used in appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners to absorb heat, thereby cooling the interior of the appliance. Historically, various substances have been used as refrigerants, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). However, due to their high Global Warming Potential (GWP) and the damage they cause to the ozone layer, these have been phased out in favor of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
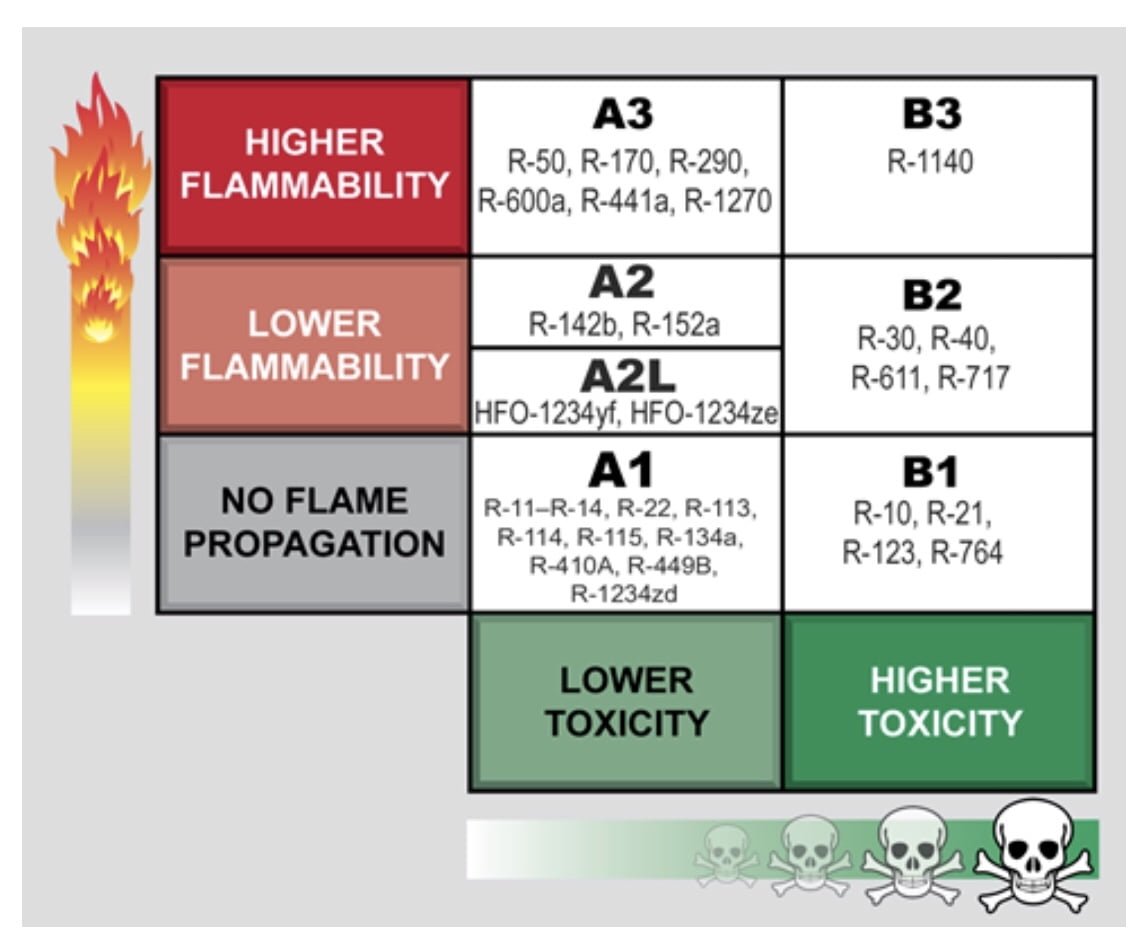
Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) are a newer class of refrigerants that have gained popularity as sustainable alternatives. They are composed of hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon, but unlike their predecessors, they contain an unsaturated carbon-carbon bond (double bond). This structural difference significantly influences their environmental and safety properties, including their flammability.

Chemical Structure and Stability:
The presence of the double bond in HFO molecules is pivotal. This bond introduces a site of unsaturation, making HFOs more reactive than fully saturated compounds. However, this does not imply that they are less stable. In fact, this chemical characteristic allows HFOs to decompose more readily in the atmosphere, leading to lower GWP.
Thermal Decomposition:
HFOs are designed to be thermally stable under typical operating conditions but decompose under extreme conditions. This decomposition process absorbs a significant amount of energy, which effectively reduces the risk of a fire starting or spreading.
HFOs vs. HFCs (Hydrofluorocarbons):
Hydrofluorocarbons, like R-134a, have been used widely due to their non-ozone depleting properties. However, they have relatively high GWPs. HFOs, such as R-1234yf, offer similar benefits but with significantly lower GWPs and are less flammable due to their chemical structure.
HFOs vs. Natural Refrigerants (Propane, Ammonia):
Natural refrigerants like propane and ammonia boast low environmental impact but come with higher risks of flammability (propane) and toxicity (ammonia). HFOs strike a balance by offering low toxicity, low flammability, and low environmental impact.
Given the critical role of refrigerants in home and commercial appliances, rigorous safety standards are in place to govern their use. For HFOs, standards such as ISO 5149 and ASHRAE 15 provide guidelines on system design, operation, and maintenance to ensure safety. Manufacturers are also continuously innovating in system design to mitigate any risks associated with refrigerant flammability.
The adoption of HFO refrigerants is on the rise, driven by their safety profile and environmental benefits. Major refrigeration and air conditioning manufacturers have transitioned to HFOs, and regulatory bodies worldwide are supporting this shift. For instance, the European Union’s F-Gas Regulation strongly advocates for the use of refrigerants with lower GWPs, bolstering the market for HFOs.
The move towards HFOs is aligned with global sustainability goals. Ongoing research aims to further enhance the efficiency and safety of these refrigerants. Innovations in refrigerant blends and advanced HVAC systems designed for optimal compatibility with HFOs are expected to drive their adoption further.
At TheKitchenApplianceDad.com, our goal is not just to provide insights into the latest trends in kitchen appliances but also to ensure you are informed about the substances and technologies that make these appliances safer and more environmentally friendly. HFO refrigerants represent a significant advancement in this direction, combining safety with sustainability. Stay tuned for more updates and in-depth analyses of how these technologies continue to evolve and impact our choices in kitchen and home appliances.